Wrapper Class ,Primitive Type
8개의 기본타입을 객체로 포장해 주는 클래스를 래퍼 클래스라고 한다.
래퍼 클래스는 각각의 타입에 해당하는 데이터를 인수로 전달받아, 해당 값을 가지는 객체로 만들어 준다.(박싱)
기본 타입 -> 래퍼 클래스 (박싱)
래퍼 클래스 -> 기본 타입 (언박싱)
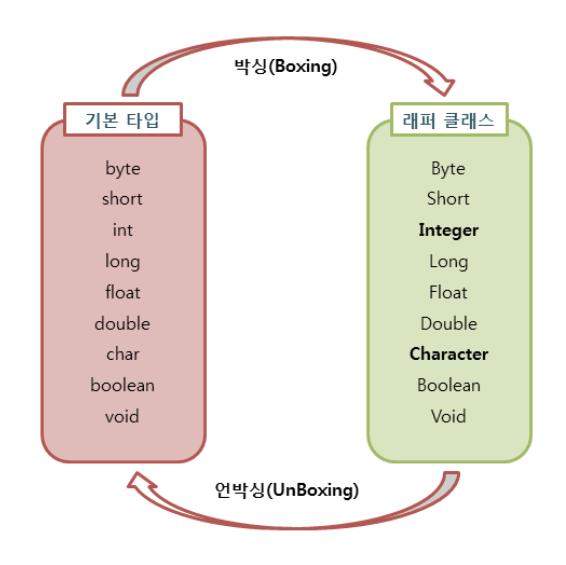
오토박싱과 오토 언방식
- 래퍼 클래스의 객체의 인스턴스로 변환하는 과정을 Boxing 이라고 한다.
- 래퍼 클래스의 인스턴스에 저장된 값을 다시 기본 타입의 데이터로 꺼내는 과정을 UnBoxing 이라고 한다.
※ 참조형과 기본형의 차이는 주소와 값의 차이로 인해 기본형 ==으로 비교가 가능하지만 참조형은 ==으로 비교할 수 가 없다(equals 사용).
JDK 1.5부터는 박싱과 언박싱이 필요한 상황에서 자바 컴파일러가 이를 자동으로 처리해 준다.
이렇게 자동화된 박싱과 언박싱을 오토 박싱(AutoBoxing)과 오토 언박싱(AutoUnBoxing)이라고 부른다.
ex ) 타입Value()- 언박싱
오토 박싱/언박싱을 통해 기본 타입과 래퍼클래스 간의 연산이 가능해졌다.
메모리 할당량의 차이
int a=100; // 4byte
Integer b=new Integet(100); // 객체(클래스 포인터, 플래그, 락,값 각각 32bit) 총 128bit- > 16byte
대략 4배의 비용이 더 든다.
기본 배열또한 객체형인데 배열의 사이즈까지 포함해 대략 5배 더 비용이든다.
+_+
이전에 참조형과 기본형에 대해 참조형은 "equals" 사용하기로 했는데 이 부분에서 첫번째 마지막에서는 true 값을 반환한다.
Integer a=127;
Integer b=127;
Integer c=128;
Integer d=128;
Integer e=-128;
Integer f=-128;
System.out.println(a==b);// true 객체생성x 캐시에 있는 값 반환
System.out.println(c==d);// false 캐시 값의 범위보다 크므로 객체 생성
System.out.println(e==f); // true 객체생성x. 캐시에 있는 값 반환Integer 래퍼 클래스에서 내부적으로 보면 -128 ~ 설정할 수 있는 최대값을 캐시에 저장해 새롭게 객체를 생성해서 반환해 주는 것이 아닌 캐시값의 범위면 바로 해당 값을 반환하므로 "=="을 사용하였을 때 true 가 나오는 것이다.
@HotSpotIntrinsicCandidate
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
// 캐시의 유효범위 값에 있는 수라면 return new Integer(i)가 아닌 캐시 값 반환.
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
private static class IntegerCache {
static final int low = -128; // default 이며 변경되지 않아야 하는 값.
static final int high;
static final Integer[] cache;
static Integer[] archivedCache;
static {
// high value may be configured by property
int h = 127;
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
try {
h = Math.max(parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue), 127);
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
h = Math.min(h, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);
} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {
// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.
}
}
.
.
.
.
.
}
일급 컬렉션 (First Class Collection)
콜렉션을 포함한 클래스는 반드시 다른 멤버 변수가 없어야 한다.
각 콜렉션은 그 자체로 포장돼 있는 것이다.
필터가 이 클래스의 일부가 된다.
이 클래스를 두 그룹으로 같이 묶는다는가 그룹의 각 원소에 규칙을 적용하느느 등의 동작을 처리 할 수 있다.
컬렉션은 매우 유용한 원시 타입이다.
Collection만을 감싸고(그 외 다른 멤버 변수가 없는 상태).
static class Order{
private final List<Order> orderList;
Order(List<Order> orderList) {
this.orderList = orderList;
}
}
Wrapping 함으로써의 이점.
- 비즈니스에 종속적인 자료구조
- Collection의 불변성 보장
- 상태와 행위를 한 곳에 관리
- 이름이 있는 컬렉션
1. 비즈니스에 종속적인 자료구조.
static class GSConveniance {
private List<IceCream> iceCreams;
public GSConveniance(List<IceCream> iceCreams) {
validateSize(iceCreams);
this.iceCreams = iceCreams;
}
private void validateSize(List<IceCream> iceCreams) {
if (iceCreams.size() >= 10) {
new RuntimeException("아이스크림은 10개 이상의 종류를 팔지 않습니다.");
}
}
}
static class CUConveniance {
private List<IceCream> iceCreams;
public CUConveniance(List<IceCream> iceCreams) {
validateSize(iceCreams);
this.iceCreams = iceCreams;
}
private void validateSize(List<IceCream> iceCreams) {
if (iceCreams.size() >= 10) {
new RuntimeException("아이스크림은 10개 이상의 종류를 팔지 않습니다.");
}
}
}gs,cu 편의점들은 각각 같은 validate조건을 사용하는데 만약 이렇게 각각의 코드에 validate가 중복이 되고 클래스의 역할이 무거워 지게 된다. 이 부분을 일급 컬렉션을 활용하여 상태와 행위을 각각 관리할 수 있다.
static class IceCream{
private List<IceCream> iceCreams;
public IceCream(List<IceCream> iceCreams) {
validateSize(iceCreams);
this.iceCreams = iceCreams;
}
private void validateSize(List<IceCream> iceCreams) {
if (iceCreams.size() >= 10) {
new RuntimeException("아이스크림은 10개 이상의 종류를 팔지 않습니다.");
}
}
}일급 컬렉션의 사용.
static class GSConveniance {
private List<IceCream> iceCreams;
public GSConveniance(List<IceCream> iceCreams) {
this.iceCreams = iceCreams;
}
}
static class CUConveniance {
private List<IceCream> iceCreams;
public CUConveniance(List<IceCream> iceCreams) {
this.iceCreams = iceCreams;
}
}
2. 불변
불변은 '재 할당'을 금지하는 것이다. 그래서 final collection에 값을 집어넣는 것이 가능하다.
다른곳에서 new를 통해 한번 더 하는 '재 할당'이 안되는 것이다.
단순히 자바에서는 final로 불변의 문제를 해결 할 수 없기에 일급 컬렉션 또는 래퍼 클래스등의 방법으로 해결해야만 한다.
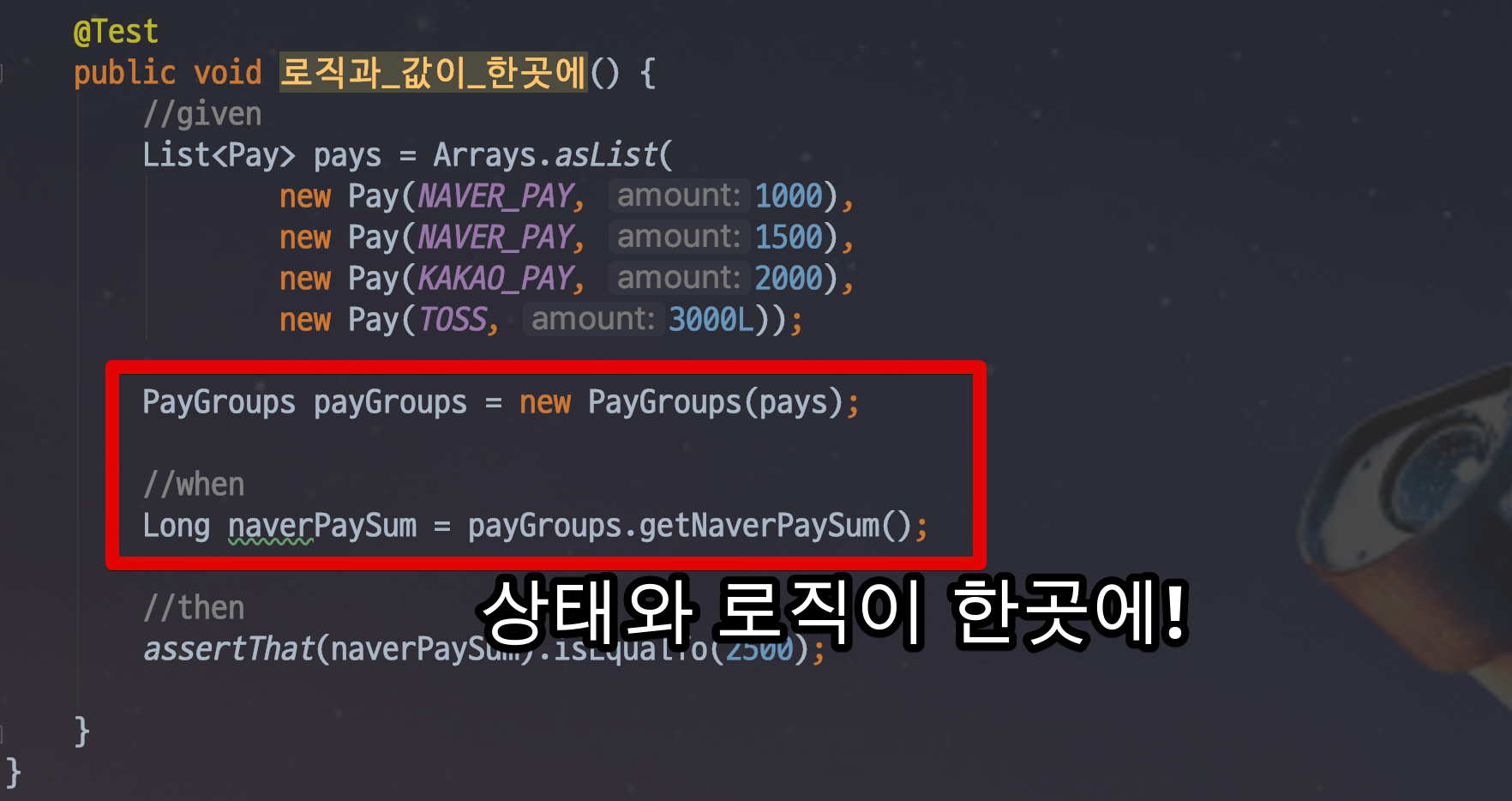
3. 상태와 행위를 한 곳에서 관리.
만약 네이버 페이의 결제 량만 보고 싶은 경우. 일급 컬렉션 내에서의 상태와 행위를 모두 한곳에서 관리 할 수 재사용이 가능하고 또는 외부에서 간단하게 코드를 작성할 수 있다.
public class PayGroups {
private List<Pay> pays;
public PayGroups(List<Pay> pays) {
this.pays = pays;
}
public Long getNaverPaySum() {
return pays.stream()
.filter(pay -> PayType.isNaverPay(pay.getPayType()))
.mapToLong(Pay::getAmount)
.sum();
}
}
'JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Garbage Collector (0) | 2021.04.25 |
|---|---|
| Reflection (0) | 2021.04.16 |
| 제네릭 타입의 컴파일 영향 (1) | 2021.04.10 |
| 자바의 compile 과정 (0) | 2021.04.04 |
| JVM 구조와 버전에 따른 변경 (0) | 2021.03.28 |

댓글